ASN.1 DER encoded data parsing by ASN1HEX class is one of the most powerful feature in jsrsasign library. Most of other ASN.1 libraries require to parse whole ASN.1 structured data to access deep inside of the structure such as SEQUENCE or SET. However it's not necessary for jsrsasign. Jsrsasign can easily point a ASN.1 object by a list of object index. From jsrsasign 8.0.21, more flexible methods getIdxbyListEx, getTLVbyListEx and getVbyListEx have been provided.
What is ASN.1?
ASN.1 is a structured binary data representation defined in ITU-T X.680 standard. Here is features of ASN.1
- can represent number, string, time, array and group.
- can represent very long length of data exceeds such as 64 bit integer limitation
- one data is represented by TAG(data type), LENGTH(value length), and VALUE
- used in communication and security protocol or formats such as X.509 digital certificate, S/MIME secure mail, private/public key formats, LDAP, Radius, SNMP or Kerberos
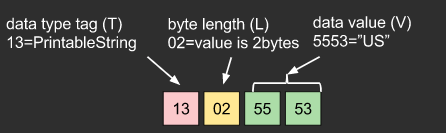
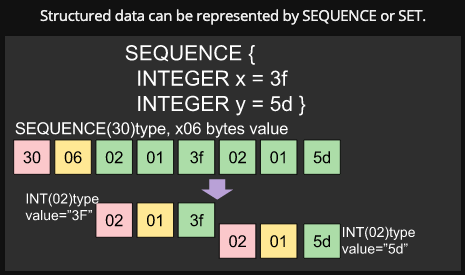
If you are new in ASN.1, you may see introduction video or page.
What is ASN1HEX?
ASN1HEX class is a simple ASN.1 parser. A hexadecimal string of ASN.1 DER data will be parsed and a string index, length bytes, value or TLV bytes will be returned by it.
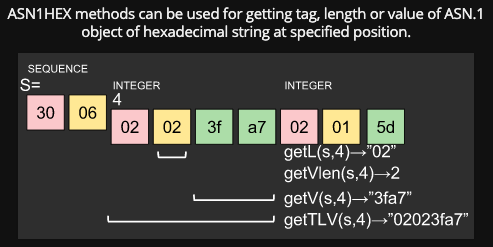
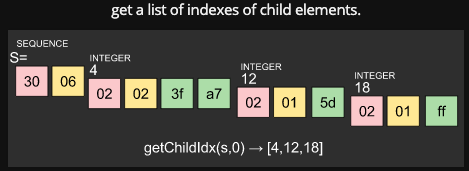
What is ASN.1 context specific tag?
Here is a ASN.1 schema of Certificate, TBSCertificate and Validity in RFC 5280.
Certificate ::= SEQUENCE {
tbsCertificate TBSCertificate,
signatureAlgorithm AlgorithmIdentifier,
signatureValue BIT STRING }
TBSCertificate ::= SEQUENCE {
version [0] EXPLICIT Version DEFAULT v1,
serialNumber CertificateSerialNumber,
signature AlgorithmIdentifier,
issuer Name,
validity Validity,
subject Name,
subjectPublicKeyInfo SubjectPublicKeyInfo,
issuerUniqueID [1] IMPLICIT UniqueIdentifier OPTIONAL,
-- If present, version MUST be v2 or v3
subjectUniqueID [2] IMPLICIT UniqueIdentifier OPTIONAL,
-- If present, version MUST be v2 or v3
extensions [3] EXPLICIT Extensions OPTIONAL
-- If present, version MUST be v3 }
Validity ::= SEQUENCE {
notBefore Time,
notAfter Time }
In above, "[0]", "[1]", "[2]" and "[3]" are called "context-specific" tag. In general, context-specific tag represents optional item. Pre-defined tag such as "PrintableString", "INTEGER" or "SEQUENCE" is called "universal tag" which has a value from 0x00 to 0x1f. Context-specific simple tag has a value from 0x80 to 0x9f represented from "[0]" to "[31]" respectively. Context-specific structured tag has a value from 0xa0 to 0xbf also represented from "[0]" to "[31]" respectively.
To learn "context-specific" tag further, please see this guide.
difference between getIdxbyList and getIdxbyListEx
In above ASN.1 schema definition, note the version field is OPTIONAL using a context specific tag [0]. So the position index of Validity will be 4 for X.509v3 certificate or 3 for X.509v1 certificate. To get netBefore value from entire hexadecimal ASN.1 string of certificate, you can use old getIdxbyList as follows. It depends on X.509 v1 or v3:
//For X.509v3
ASN1HEX.getVbyList(<<CERTHEX>>, 0, [0, 4, 0])
//Or for X.509v1
ASN1HEX.getVbyList(<<CERTHEX>>, 0, [0, 3, 0])
When you use new getIdxbyListEx, position index will be always 3 since all context specific tag will be treated as a optional item and skipped to count index:
ASN1HEX.getVbyListEx(<<CERTHEX>>, 0, [0, 3, 0])
To access context specific tag in new getIdxbyListEx use a tag string (ex. "[3]") instead of index number. You can refer extension field as follows. You don't need to care about optional field such as version or issuerUniqueID:
ASN1HEX.getIdxbyListEx(<<CERTHEX>>, 0, [0, "[3]"])
I hope you can handle context-specific tag more easily by new getIdxbyListEx. You can also dig into "OctetString Encapsulated", "BitString Encapsulated" or "Explicit Context Specific Tag" which has a ASN.1 TLV structure in its ASN.1 value(V) by the same way as above.